Ledmi M, Moumen H, Siam A, Haouassi H, Azizi N.
A Discrete Crow Search Algorithm for Mining Quantitative Association Rules. International Journal of Swarm Intelligence Research (IJSIR) [Internet]. 2021;12 (4) :101-124.
Publisher's VersionAbstractAssociation rules are the specific data mining methods aiming to discover explicit relations between the different attributes in a large dataset. However, in reality, several datasets may contain both numeric and categorical attributes. Recently, many meta-heuristic algorithms that mimic the nature are developed for solving continuous problems. This article proposes a new algorithm, DCSA-QAR, for mining quantitative association rules based on crow search algorithm (CSA). To accomplish this, new operators are defined to increase the ability to explore the searching space and ensure the transition from the continuous to the discrete version of CSA. Moreover, a new discretization algorithm is adopted for numerical attributes taking into account dependencies probably that exist between attributes. Finally, to evaluate the performance, DCSA-QAR is compared with particle swarm optimization and mono and multi-objective evolutionary approaches for mining association rules. The results obtained over real-world datasets show the outstanding performance of DCSA-QAR in terms of quality measures.
Aouadj W, Abdessemed MR, Seghir R.
Discrete Large-scale Multi-Objective Teaching-Learning-Based Optimization Algorithm, in
Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Networking, Information Systems & Security. ; 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractThis paper presents a teaching-learning-based optimization algorithm for discrete large-scale multi-objective problems (DLM-TLBO). Unlike the previous variants, the learning strategy used by each individual and the acquired knowledge are defined based on its level. The proposed approach is used to solve a bi-objective object clustering task (B-OCT) in a swarm robotic system, as a case study. The simple robots have as mission the gathering of a number of objects distributed randomly, while respecting two objectives: maximizing the clustering quality, and minimizing the energy consumed by these robots. The simulation results of the proposed algorithm are compared to those obtained by the well-known algorithm NSGA-II. The results show the superiority of the proposed DLM-TLBO in terms of the quality of the obtained Pareto front approximation and convergence speed.
Mazouz F, Belkacem S, Colak I.
DPC-SVM of DFIG Using Fuzzy Second Order Sliding Mode Approach. International Journal of Smart Grid-ijSmartGrid [Internet]. 2021;5 (4) :174-182.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The direct control power (DPC) of the of the double feed induction generator (DFIG) using conventional controllers based on PI regulators is characterized by poor results: Robustness properties are not guaranteed in the face of parametric uncertainties and strong ripple of the powers. From the best evoked control techniques presented in this field to overcome these drawbacks, we will study some improvement variants such as the use of The second order sliding mode control (SOSMC) developed on the basis of the super twisting torsion algorithm (STA) associated with the fuzzy logic control to obtain (FSOSMC) in order to obtain acceptable performance. Finally, the effectiveness of the planned control system is studied using Matlab/Simulink. The proposed method that not only reduces power ripples, but also improves driving dynamics by making it less sensitive to parameter uncertainty.
Taguelmimt R, Beghdad R.
DS-kNN: An Intrusion Detection System Based on a Distance Sum-Based K-Nearest Neighbors. International Journal of Information Security and Privacy (IJISP) [Internet]. 2021;15 (2) :131-144.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
On one hand, there are many proposed intrusion detection systems (IDSs) in the literature. On the other hand, many studies try to deduce the important features that can best detect attacks. This paper presents a new and an easy-to-implement approach to intrusion detection, named distance sum-based k-nearest neighbors (DS-kNN), which is an improved version of k-NN classifier. Given a data sample to classify, DS-kNN computes the distance sum of the k-nearest neighbors of the data sample in each of the possible classes of the dataset. Then, the data sample is assigned to the class having the smallest sum. The experimental results show that the DS-kNN classifier performs better than the original k-NN algorithm in terms of accuracy, detection rate, false positive, and attacks classification. The authors mainly compare DS-kNN to CANN, but also to SVM, S-NDAE, and DBN. The obtained results also show that the approach is very competitive.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
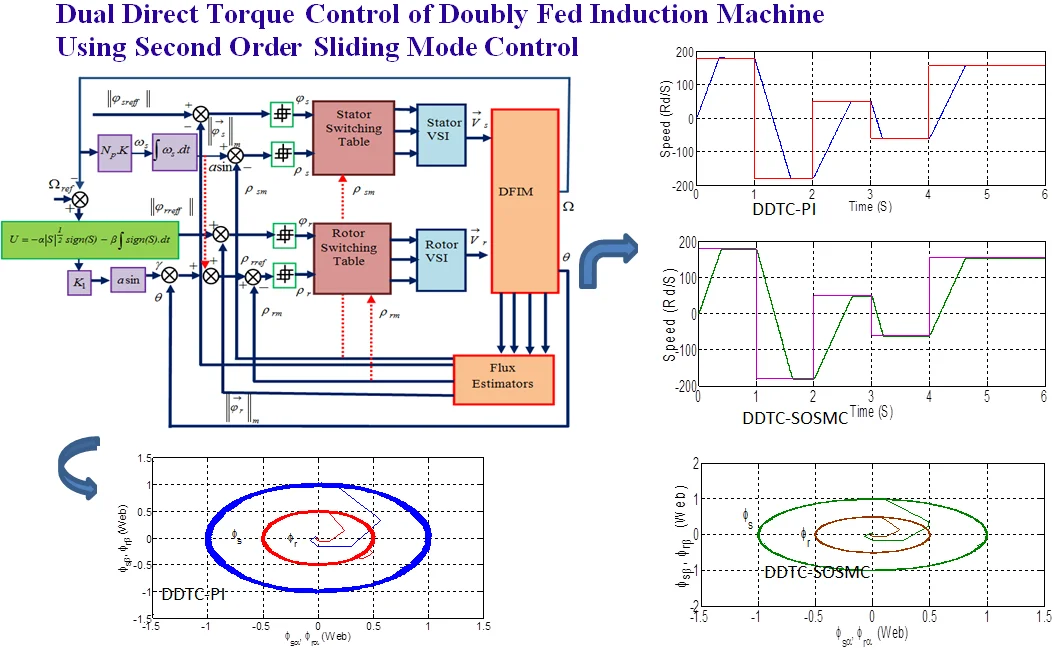
Boumaraf F, BOUTABBA T, Belkacem S.
Dual direct torque control of doubly fed induction machine using second order sliding mode control. Journal of Measurements in Engineering [Internet]. 2021;9 (1) :1-12.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper a dual direct torque control (DDTC) strategy with second-order sliding mode control (SOSMC) controller of the doubly fed Induction motor (DFIM) is presented in order to overcome some drawback such as ripples in torque, flux and to improve dual direct torque control (DDTC) performance toward the electrical parameters variations. This control strategy used in the doubly fed induction machine supplied, coupled by two voltage source inverters in rotor and stator sides witches are linked to two switching tables in order to determined the rotor and stator flux vector control. This controller based on super-twisting algorithm (STA). Comparative results between a classical controller (PI) and the proposed controller can prove the very satisfactory performance and robustness of this new controller.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Beghzim H, Karech T, Bouzid T.
The Effect of Faults on the Behaviour of the Earth Dam–Case Study of the Ourkiss Dam. (Preprint). Research Square [Internet]. 2021.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The analysis of the failure due to the effect of the propagation of normal and reversed faults with different angles of inclination and by sliding through the Ourkiss dam isstudied numerically. Mainly at the end of construction and at the highest water level, for this purpose the non-linear finite difference method is used considering four fault angles of inclination, activated at the center of the base of the embankment.
The results of the study show that the shear stress values increase with the increase of the vertical base displacement imposed in both conditions of the dam state, and this for both normal and overturned faults.
Zine A, Kadid A, Zatar A.
Effect of Masonry Infill Panels on the Seismic Response of Reinforced Concrete Frame Structures. Civil Engineering Journal [Internet]. 2021;7 (11) :1853-1867.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The present work concerns the numerical investigation of reinforced concrete frame buildings containing masonry infill panel under seismic loading that are widely used even in high seismicity areas. In seismic zones, these frames with masonry infill panels are generally considered as higher earthquake risk buildings. As a result there is a growing need to evaluate their level of seismic performance. The numerical modelling of infilled frames structures is a complex task, as they exhibit highly nonlinear inelastic behaviour, due to the interaction of the masonry infill panel and the surrounding frame. The available modelling approaches for masonry infill can be grouped into two principal types; Micro models and Macro models. A two dimensional model of the structure is used to carry out non-linear static analysis. Beams and columns are modelled as non-linear with lumped plasticity where the hinges are concentrated at both ends of the beams and the columns. This study is based on structures with design and detailing characteristics typical of Algerian construction model. In this regard, a non-linear pushover analysis has been conducted on three considered structures, of two, four and eight stories. Each structure is analysed as a bare frame and with two different infill configurations (totally infilled, and partially infilled). The main results that can be obtained from a pushover analysis are the capacity curves and the distribution of plastic hinges in structures. The addition of infill walls results in an increase in both the rigidity and strength of the structures. The results indicate that the presence of non-structural masonry infills can significantly modify the seismic response of reinforced concrete "frames". The initial rigidity and strength of the fully filled frame are considerably improved and the patterns of the hinges are influenced by structural elements type depending on the dynamic characteristics of the structures.
Rahem A, Djarir Y, Noureddine L, Tayeb B.
Effect of masonry infill walls with openings on nonlinear response of steel frames. Civil Engineering Journal [Internet]. 2021;7 (2) :278-291.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The infill walls are usually considered as nonstructural elements and, thus, are not taken into account in analytical models. However, numerous researches have shown that they can significantly affect the seismic response of the structures. The aim of the present study is to examine the role of masonry infill on the damage response of steel frame without and with various types of openings systems subjected to nonlinear static analysis and nonlinear time history analysis. For the purposes of the above investigation, a comprehensive assessment is conducted using twelve typical types of steel frame without masonry, with full masonry and with different heights and widths of openings. The results revealed that the influence of the successive earthquake phenomenon on the structural damage is larger for the infill buildings compared to the bare structures. Furthermore, when buildings with masonry infill are analyzed for seismic sequences, it is of great importance to account for the orientation of the seismic motion. The nonlinear static response indicated that the opening area has an influence on the maximal strength, the ductility and the initial rigidity of these frames. But the shape of the opening will not influence the global behavior. Then, the nonlinear time history analysis indicates that the global displacement is greatly decreased and even the behavior of the curve is affected by the earthquake intensity when opening is considered.
Fourar I, Benmachiche A-H, Abboudi S.
Effect of material and geometric parameters on natural convection heat transfer over an eccentric annular-finned tube. International Journal of Ambient Energy [Internet]. 2021;42 (8) :929-939.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this work, the performance of an eccentric annular finned tube heat exchanger under natural convection conditions has been investigated numerically. The objective of the study is to analyse the effect of eccentric coefficient on the rate heat flux as a function of the fin material, diameter, spacing and thicknesses. To perform the numerical simulations, 3D ANSYS FLUENT computational fluid dynamics has been used. The study has been conducted in laminar flow across the single annular finned tube with Rayleigh numbers within of (4 × 104−7 × 104). It is concluded that the eccentricity effect appears better in high thermal conductivity materials with small fin diameter. Regardless of the fin eccentricity, thick fins produce the best heat transfer.
Zeguerrou N, Adjroudi R, Bachir AS, El-Okki MEH.
Effect of the poultry droppings waste on the different life stage of Eisenia fetida (Savigny, 1826). International Journal of Environment and Waste Management [Internet]. 2021;28 (2) :131-148.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
This paper aims to evaluate the effect of poultry droppings waste on the different life stage of Eisenia fetida earthworm to protect them from hazardous doses. Adults, juveniles and cocoons were exposed during 90 days to increased doses of poultry droppings (0, 10, 20, 50 and 100 g), added to 250 g of culture substrate. The biological parameters, like mortality, body length, fresh biomass, and cocoons hatching were affected by the organic waste doses and the exposure time. Both poultry droppings doses 10 g (4%) and 20 g (8%) were the less toxic to the cocoons hatching and to the adults' and juveniles' growth. While the two doses, 50 g (20%) and 100 g (40%), had a negative impact on the cocoon hatchability and a toxic effect on the juveniles and adults. Otherwise, the poultry droppings dose 100 g was lethal for the all life stage of E. fetida.
Mansouri T, Boufarh R, Saadi D.
Effects of underground circular void on strip footing laid on the edge of a cohesionless slope under eccentric loads. Soils and RocksSoils and Rocks [Internet]. 2021;44 (1).
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Owing to the comeback of small-scale models, this paper presents results of an experimental study based on the effect of underground circular voids on strip footing placed on the edge of a cohesionless slope and subjected to eccentric loads. The bearing capacity-settlement relationship of footing on the slope and impact of diverse variables are expressed using dimensionless parameters such as the top vertical distance of the void from the base of footing, horizontal space linking the void-footing centre, and load eccentricity. The results verified that the stability of strip footing is influenced by the underground void, as well as the critical depth between the soil and top layer of the void. The critical horizontal distance between the void and the centre was also affected by the underground void. Furthermore, the results also verified that the influence of the void appeared insignificant when it was positioned at a depth or eccentricity equal to twice the width of footing.
Boubiche S, Bilami A, Boubiche D-E.
An Efficient Approach for Big Data Aggregation Mechanism in Heterogeneous Wireless Connected Sensor Networks. Wireless Personal Communications [Internet]. 2021;118 :1405-1437.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Recently and due to the impressive growth in the amounts of transmitted data over the heterogeneous sensor networks and the emerged related technologies especially the Internet of Things in which the number of the connected devices and the data consumption are remarkably growing, big data has emerged as a widely recognized trend and is increasingly being talked about. The term big data is not only about the volume of data, but also refers to the high speed of transmission and the wide variety of information that is difficult to collect, store and process using the available classical technologies. Although the generated data by the individual sensors may not appear to be significant, all the data generated through the many sensors in the connected sensor networks are able to produce large volumes of data. Big data management imposes additional constraints on the wireless sensor networks and especially on the data aggregation process, which represents one of the essential paradigms in wireless sensor networks. Data aggregation process can represent a solution to the problem of big data by allowing data from different sources to be combined to eliminate the redundant ones and consequently reduce the amounts of data and the consumption of the available resources in the network. The main objective of this work is to propose a new approach for supporting big data in the data aggregation process in heterogeneous wireless sensor networks. The proposed approach aims to reduce the data aggregation cost in terms of energy consumption by balancing the data loads on the heterogeneous nodes. The proposal is improved by integrating the feedback control closed loop to reinforce the balance of the data aggregation load on the nodes, maintaining therefore an optimal delay and aggregation time.
Sulaiman A-M, Muna M, Kenza B, Sara H, Djohra H, Hala L, Christiaan S, Elsadeg S, Nouran T.
Epidemiology and demographics of juvenile idiopathic arthritis in Africa and Middle East. Pediatric Rheumatology [Internet]. 2021;19.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (JIA) is a group of chronic heterogenous disorders that manifests as joint inflammation in patients aged <16 years. Globally, approximately 3 million children and young adults are suffering from JIA with prevalence rates consistently higher in girls. The region of Africa and Middle East constitute a diverse group of ethnicities, socioeconomic conditions, and climates which influence the prevalence of JIA. There are only a few studies published on epidemiology of JIA in the region. There is an evident paucity of adequate and latest data from the region. This review summarizes the available data on the prevalence of JIA and its subtypes in Africa and Middle East and discusses unmet needs for patients in this region. A total of 8 journal publications were identified concerning epidemiology and 42 articles describing JIA subtypes from Africa and Middle East were included. The prevalence of JIA in Africa and Middle East was observed to be towards the lower range of the global estimate. We observed that the most prevalent subtype in the region was oligoarticular arthritis. The incidence of uveitis and anti-nuclear antibody (ANA) positivity were found to be lower as compared to the incidence from other regions. There is a huge unmet medical need in the region for reliable epidemiological data, disease awareness, having regional and local treatment guidelines and timely diagnosis. Paucity of the pediatric rheumatologists and economic disparities also contribute to the challenges regarding the management of JIA.
Cherak Z, Loucif L, Moussi A, Rolain J-M.
Epidemiology of mobile colistin resistance (mcr) genes in aquatic environments. Journal of Global Antimicrobial Resistance [Internet]. 2021;27 :51-62.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Colistin is one of the last-line therapies against multidrug-resistant Gram-negative pathogens, especially carbapenemase-producing isolates, making resistance to this compound a major global public-health crisis. Until recently, colistin resistance in Gram-negative bacteria was known to arise only by chromosomal mutations. However, a plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism was described in late 2015. This mechanism is encoded by different mobile colistin resistance (mcr) genes that encode phosphoethanolamine (pEtN) transferases. These enzymes catalyse the addition of a pEtN moiety to lipid A in the bacterial outer membrane leading to colistin resistance. MCR-producing Gram-negative bacteria have been largely disseminated worldwide. However, their environmental dissemination has been underestimated. Indeed, water environments act as a connecting medium between different environments, allowing them to play a crucial role in the spread of antibiotic resistance between the natural environment and humans and other animals. For a better understanding of the role of such environments as reservoirs and/or dissemination routes of mcr genes, this review discusses primarily the various water habitats contributing to the spread of antibiotic resistance. Thereafter, we provide an overview of existing knowledge regarding the global epidemiology of mcr genes in water environments. This review confirms the global distribution of mcr genes in several water environments, including wastewater from different origins, surface water and tap water, making these environments reservoirs and dissemination routes of concern for this resistance mechanism.
BOUAFIA W.
Evaluation des activités biologiques et caractérisation phytochimique de la plante Ephedra altissima Desf. Biologie des organismes [Internet]. 2021.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Ephedra altissima Desf. est une plante médicinale de la famille des Ephedraceae, largement utilisée en médecine traditionnelle pour le traitement des maladies respiratoires et le diabète. L’objectif de la présente étude est l’évaluation des activités biologiques in vitro et la caractérisation phytochimique des extraits (éther de pétrole, acétate d’éthyle et n-butanol) obtenus à partir de la plante Ephedra altissima. Des dosages colorimétriques ont été effectués pour révéler la présence de différentes classes de métabolites secondaires. La détermination des teneurs en polyphénols, flavonoïdes et tanins condensés a été réalisée par des dosages spectrophotométriques. L’activité antioxydante a été évaluée par huit méthodes différentes, l’activité anti-artéritiques a été réalisée par la méthode d’inhibition de la dénaturation du sérum d’albumine bovin, les activités inhibitrices de l’α-amylase et de la lipase pancréatique in vitro ont été estimées par des méthodes colorimétriques en utilisant de l'amidon et du p-nitrophényl butyrate en tant que substrats. Les conditions physiologiques de la digestion humaine ont été simulées par le modèle de la digestion gastro-intestinale (DGI) in vitro. L’activité antibactérienne a été déterminée par la méthode de diffusion sur disques en milieu gélosé contre sept souches bacteriennes. L’analyse et la quantification des composés phénoliques ont été effectuées par LC-DAD-ESI/MS. L’investigation phytochimique de l’extrait n-butanolique a été réalisée par l’utilisation en alternance de diverses méthodes chromatographiques (VLC, CC, CCE et CCM). Les structures des deux composés isolés A et B ont été identifiées par analyse spectroscopique ESI-MS, l’UV et la RMN dans ses multiples techniques, RMN 1H, RMN 13C, et RMN 2D (COSY, HSQC, HMBC et TOCSY). A l’issue de ces travaux, nous retiendrons la richesse de cette plante en métabolites secondaires. En effet, l’extrait AcOEt présente la teneur la plus élevée en polyphénols (125,62 μg EAG mg-1), et le n-BuOH possède la teneur la plus élevée en flavonoïdes (19,18 μg EQ mg-1). Tous les extraits ont des activités antioxydantes dans divers systèmes et l'extrait aqueux a montré une bonne activité antioxydante par la méthode potentiométrique. L’extrait AcOEt exhibe la plus forte activité anti-artéritique, activités inhibitrices de de l’α-amylase et de la lipase pancréatique avec des valeurs de CI50 (126,4 ± 2,36, 8,07 ± 0,15 et 289,1 ± 0,53 μg/ml) respectivement. Tous les extraits testés exercent une activité antibactérienne dose dépendante contre au moins trois souches avec des CMI allant de (3,12 à 50 μg/ml). L’analyse par LC-DAD-ESI/MS a permis de détecter la présence de dix-neuf composés différents, huit sont des acides phénoliques simples et des dérivés d'acide phénolique, et onze sont des flavonoïdes liés à des groupes glycosyles. L’investigation phytochimique réalisée sur l’extrait n-batanolique conduit à l’isolement et identification structurale de deux flavonoides glycosylés nommés : Isorhamnétine 3-O- α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1’’’-6’’)- β-D-galactopyranoside et Kaempférol 3-O- α-L-rhamnopyranosyl (1’’’-6’’)- β-D-glucopyranoside.
Alloui N, Sellaoui S, Ayachi A, Bennoune O.
Evaluation of biosecurity practices in a laying hens farm using Biocheck. UGent. Multidisciplinary Science Journal [Internet]. 2021;3 (3) :e2021014-e2021014.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The Biocheck.UGent scoring system was developed to measure and quantify the level of biosecurity in animal husbandry. This tool is composed of all the relevant elements of biosecurity in poultry farms (broilers and laying hens) and is subdivided into external and internal biosecurity. The peculiarity of this scoring system is that it takes into account the relative importance of the different aspects of biosecurity, resulting in a risk-weighted score. The biosecurity scores obtained are provided immediately after completing the questionnaire and the scores for each sub-category can be compared to global averages to allow the poultry farmer to compare the results obtained and correct any anomalies that are on their farm. In Algeria, preliminary results from a survey in poultry houses of 30.000 laying hens show a wide range of biosecurity levels on that farm, with internal biosecurity scores ranging from 6 to 72% and external biosecurity scores ranging from 28 to 92% in the subgroups. The overall scores were 50% and 54%, respectively. These early results show that despite the well-known importance of biosecurity, there is a lack of implementation of many biosecurity measures.
Mohamadi A, Demdoum A, Bouaicha F, MENANI MR.
Evaluation of the quality of groundwater for its appropriateness for irrigation purposes using Water Quality Index (WQI), Mchira-Teleghma aquifer case study, northeastern Algeria. Sustainable Water Resources Management [Internet]. 2021;7 :1-16.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The Mio-Plio-Quaternary groundwater of Mchira-Teleghma suffers from an increasing rate of salinity especially in the northwestern part. To identify the reason for the water’s salinity and its aptitude for irrigation, physico-chemical analyses of 20 water samples, which were based on the different physical and chemical parameters (electric conductivity EC, pH, Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, K+, HCO3−, Cl−, SO42−, NO3− and Sr2+), were carried out during the period of October 2015. This study showed disquieting anomalies of electric conductivity that reached the value of 4376.14 µS cm−1. The statistical analyses, the multivariate statistics: the principal component analysis, Q-mode cluster analyses, Sr2+/Ca2+ ratio and water type showed that the hydrochemistry of Mchira-Teleghma groundwater is controlled by the dissolution of carbonate rocks and the leaching of evaporite processes, which proved that these anomalies of the MPQ groundwater’s salinity of Mchira-Teleghma are mainly determined by the leaching of Triassic gypsum formations process. This hydrogeochemical process generates an unsuitable quality of water based on Wilcox’s and Water Quality Index’s methods, whereas Richard’s method classifies all water samples to C3S1 and C4S1 classes as they are recommended to be used with salt-tolerant species in well-drained and leached soils.
Bensaad M-S, Dassamiour S, Hambaba L, Kahoul M-A, Benhoula M.
Evidence of anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer properties of aerial parts of Centaurea tougourensis Boiss. and Reut. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research [Internet]. 2021;20 (8).
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Purpose: To determine the anti-inflammatory and anti-ulcer properties of the aerial parts of Centaurea tougourensis Boiss. & Reut.
Methods: The effects of n-butanol (n-BuOH) extract of the aerial part of Centaurea tougourensis on carrageenan-induced paw edema and ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage were determined at 2 doses (200 and 400 mg/kg, po) in a mouse model. For each test, the animals were randomly divided into negative and positive control groups, as well as extract-treated groups. The mice were observed for any sign of inflammation for a period of 24h.
Results: Reduction of paw edema by C. tougourensis extract was highly significant (p < 0.001) at a dose of 400 mg/kg 24 h after carrageenan injection, with 55.26 % inhibition, followed very closely by 53.15 % inhibition at the dose of 200 mg/kg; indomethacin group showed an inhibition of 60 %. Histological examination supported the inhibition results. A significant reduction in inflammation by the extract at a dose of 400 mg/kg was also observed. No sign of ulcer was observed with C. tougourensis at the two doses (200 and 400 mg/kg). The total polyphenol content of the n-BuOH extract was 85.44 цg gallic acid equivalent/mg of extract. Tannins were the most abundant fraction (51.87 цg tannic acid equivalent/mg of extract), followed by flavonoids (25.55 цg quercetin equivalent/mg of extract).
Conclusion: The results indicate that C. tougourensis may have potential beneficial effects in the treatment of diseases associated with inflammation and pain, besides its protective effect on the gastrointestinal tract.