2021
Mazouz F, Belkacem S, Colak I.
DPC-SVM of DFIG Using Fuzzy Second Order Sliding Mode Approach. International Journal of Smart Grid-ijSmartGrid [Internet]. 2021;5 (4) :174-182.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The direct control power (DPC) of the of the double feed induction generator (DFIG) using conventional controllers based on PI regulators is characterized by poor results: Robustness properties are not guaranteed in the face of parametric uncertainties and strong ripple of the powers. From the best evoked control techniques presented in this field to overcome these drawbacks, we will study some improvement variants such as the use of The second order sliding mode control (SOSMC) developed on the basis of the super twisting torsion algorithm (STA) associated with the fuzzy logic control to obtain (FSOSMC) in order to obtain acceptable performance. Finally, the effectiveness of the planned control system is studied using Matlab/Simulink. The proposed method that not only reduces power ripples, but also improves driving dynamics by making it less sensitive to parameter uncertainty.
Taguelmimt R, Beghdad R.
DS-kNN: An Intrusion Detection System Based on a Distance Sum-Based K-Nearest Neighbors. International Journal of Information Security and Privacy (IJISP) [Internet]. 2021;15 (2) :131-144.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
On one hand, there are many proposed intrusion detection systems (IDSs) in the literature. On the other hand, many studies try to deduce the important features that can best detect attacks. This paper presents a new and an easy-to-implement approach to intrusion detection, named distance sum-based k-nearest neighbors (DS-kNN), which is an improved version of k-NN classifier. Given a data sample to classify, DS-kNN computes the distance sum of the k-nearest neighbors of the data sample in each of the possible classes of the dataset. Then, the data sample is assigned to the class having the smallest sum. The experimental results show that the DS-kNN classifier performs better than the original k-NN algorithm in terms of accuracy, detection rate, false positive, and attacks classification. The authors mainly compare DS-kNN to CANN, but also to SVM, S-NDAE, and DBN. The obtained results also show that the approach is very competitive.
Taguelmimt R, Beghdad R.
DS-kNN: An Intrusion Detection System Based on a Distance Sum-Based K-Nearest Neighbors. International Journal of Information Security and Privacy (IJISP) [Internet]. 2021;15 (2) :131-144.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
On one hand, there are many proposed intrusion detection systems (IDSs) in the literature. On the other hand, many studies try to deduce the important features that can best detect attacks. This paper presents a new and an easy-to-implement approach to intrusion detection, named distance sum-based k-nearest neighbors (DS-kNN), which is an improved version of k-NN classifier. Given a data sample to classify, DS-kNN computes the distance sum of the k-nearest neighbors of the data sample in each of the possible classes of the dataset. Then, the data sample is assigned to the class having the smallest sum. The experimental results show that the DS-kNN classifier performs better than the original k-NN algorithm in terms of accuracy, detection rate, false positive, and attacks classification. The authors mainly compare DS-kNN to CANN, but also to SVM, S-NDAE, and DBN. The obtained results also show that the approach is very competitive.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
Boutabba T, Fatah A, Sahraoui H, Khamari D, Benlaloui I, Drid S, Chrifi-Alaoui L.
dSPACE Real-Time Implementation of Maximum Power Point Tracking Based on Kalman Filter Structure using Photovoltaic System Emulator. 2021 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD) [Internet]. 2021 :1-6.
Publisher's VersionAbstractIn this paper, we propose an implementation of a new technique of power maximization using a photovoltaic system emulator. The PV system design and its performance evaluation test before installation would be both costly and time-consuming. To overcome this problem the use of an emulator adds more performance and efficiency in the laboratory. Also, by measuring the voltage and current from the PV emulator the characteristic I-V and P-V are extract.The need to consider the measure power state is strongly nonlinear distribution curve with noise. For that reason, to establish and to detect the power value, measurement equations and dynamic equations proposed MPPT control strategy based on Kalman filter algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the strategy is verified by simulation and experiment. This algorithm was experimentally implemented. Data acquisition and control system were implemented using dSPACE1103. The results show that the Kalman filter MPPT work accurately and successfully under the change of solar irradiation.
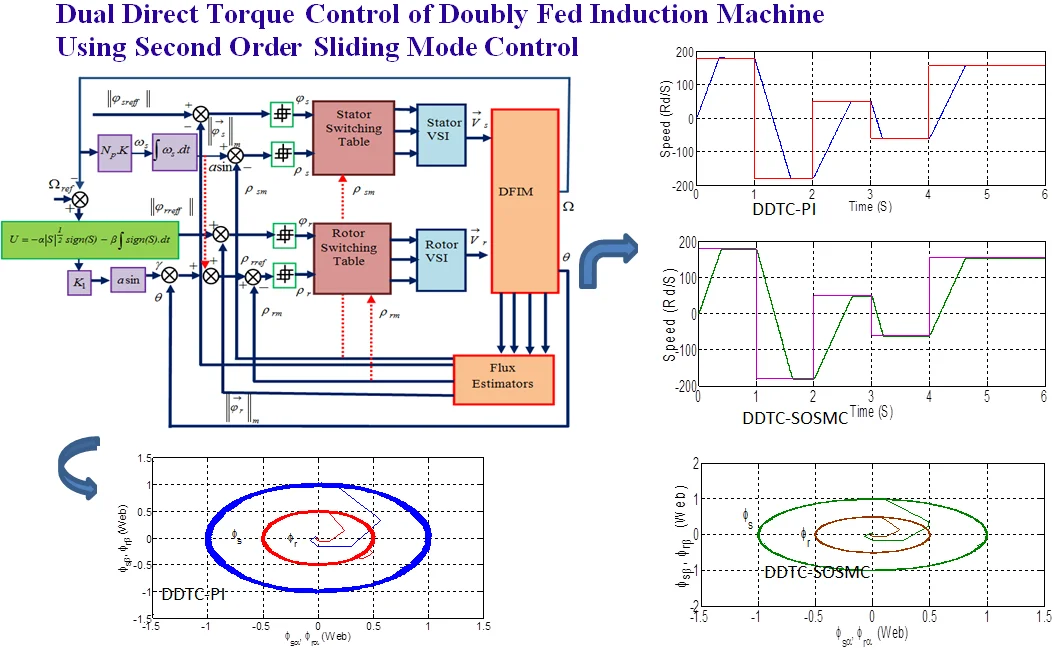
Boumaraf F, BOUTABBA T, Belkacem S.
Dual direct torque control of doubly fed induction machine using second order sliding mode control. Journal of Measurements in Engineering [Internet]. 2021;9 (1) :1-12.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper a dual direct torque control (DDTC) strategy with second-order sliding mode control (SOSMC) controller of the doubly fed Induction motor (DFIM) is presented in order to overcome some drawback such as ripples in torque, flux and to improve dual direct torque control (DDTC) performance toward the electrical parameters variations. This control strategy used in the doubly fed induction machine supplied, coupled by two voltage source inverters in rotor and stator sides witches are linked to two switching tables in order to determined the rotor and stator flux vector control. This controller based on super-twisting algorithm (STA). Comparative results between a classical controller (PI) and the proposed controller can prove the very satisfactory performance and robustness of this new controller.
Boumaraf F, BOUTABBA T, Belkacem S.
Dual direct torque control of doubly fed induction machine using second order sliding mode control. Journal of Measurements in Engineering [Internet]. 2021;9 (1) :1-12.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper a dual direct torque control (DDTC) strategy with second-order sliding mode control (SOSMC) controller of the doubly fed Induction motor (DFIM) is presented in order to overcome some drawback such as ripples in torque, flux and to improve dual direct torque control (DDTC) performance toward the electrical parameters variations. This control strategy used in the doubly fed induction machine supplied, coupled by two voltage source inverters in rotor and stator sides witches are linked to two switching tables in order to determined the rotor and stator flux vector control. This controller based on super-twisting algorithm (STA). Comparative results between a classical controller (PI) and the proposed controller can prove the very satisfactory performance and robustness of this new controller.

Boumaraf F, BOUTABBA T, Belkacem S.
Dual direct torque control of doubly fed induction machine using second order sliding mode control. Journal of Measurements in Engineering [Internet]. 2021;9 (1) :1-12.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper a dual direct torque control (DDTC) strategy with second-order sliding mode control (SOSMC) controller of the doubly fed Induction motor (DFIM) is presented in order to overcome some drawback such as ripples in torque, flux and to improve dual direct torque control (DDTC) performance toward the electrical parameters variations. This control strategy used in the doubly fed induction machine supplied, coupled by two voltage source inverters in rotor and stator sides witches are linked to two switching tables in order to determined the rotor and stator flux vector control. This controller based on super-twisting algorithm (STA). Comparative results between a classical controller (PI) and the proposed controller can prove the very satisfactory performance and robustness of this new controller.

Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.