Bouhoufani O, Hamchi I.
Coupled System of Nonlinear Hyperbolic Equations with Variable-Exponents: Global Existence and Stability (vol 17, 166, 2020). MEDITERRANEAN JOURNAL OF MATHEMATICS [Internet]. 2021;18.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we consider a coupled system of two nonlinear hyperbolic equations with variable-exponents in the damping and source terms. Under suitable assumptions on the intial data and the variable exponents, we prove a global existence theorem, using the Stable-set method. Then, we establish a decay estimate of the solution energy, by Komornik’s integral approach.
Nacer F, DRIDI H.
The Creation of Development Regions as Input to the Regional Development in the North-East Wilayas (Departments) of Algeria. Analele Universităţii din Oradea, Seria GeografieAnalele Universităţii din Oradea, Seria Geografie [Internet]. 2021;31 :1-10.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
-
The research paper aims to create development region, as itis a means for reorganizing the potential for development, as the research work dealt with a systematic vision based on the merging of the results of statistical analysis with the principles adopted in regional divisions, we have identified three regions with different developmental characteristics; the north eastern developmental region, the Constantine development region and the eastern high plains region. The results of the work are shown in a map of development regions were the final outputs of the research paper are prepared.
-
Copyright of Annals of the University of Oradea, Geography Series / Analele Universitatii din Oradea, Seria Geografie is the property of University of Oradea, Department of Geography, Tourism & Territorial Planning and its content may not be copied or emailed to multiple sites or posted to a listserv without the copyright holder's express written permission. However, users may print, download, or email articles for individual use. This abstract may be abridged. No warranty is given about the accuracy of the copy. Users should refer to the original published version of the material for the full abstract.
Boubiche D-E, Athmania D, Boubiche S, Homero T-C.
Cybersecurity issues in wireless sensor networks: current challenges and solutions. Wireless Personal Communications [Internet]. 2021;117 :177-213.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Wireless sensor networks are deployed without predefined infrastructure and are generally left unattended. Indeed, the vulnerability of the wireless sensor networks to attacks comes principally from their inherent characteristics. As the data are transmitted over the air, it is very easy for an adversary to spy on traffic. Also, to meet the strict budgetary requirements, the sensor nodes tend to not be tamperproof and thus offer no protection against security attacks. Alongside with these vulnerabilities, the human intervention is always not allowed to deal with adversaries who attempt to compromise the network. Therefore, security systems are mainly needed to secure the network and ensure the protection against security threats. Indeed, cryptographic based systems are generally used to ensure security. However, due to the lack of memory and power (low computing, limited energy reserves) of the sensor nodes, most of these approaches are not suitable. Therefore, providing security while respecting the specific constraints of the sensors, represents one of the most important research issue in wireless sensor networks. Indeed, several studies have been conducted these last decades to propose lightweight and efficient security protocols for wireless sensor networks. In this paper, we review the most leading protocols and classify them based the addressed security issue. Also, we outline the main security constraints and challenges and present the future research directions based on the emerged application fields.
Mohammed AS, Smail R.
A decision loop for situation risk assessment under uncertainty: A case study of a gas facility. Petroleum [Internet]. 2021;7 (3) :343-348.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
This paper presents a decision-making support system for situation risk assessment associated with critical alarms conditions in a gas facility. The system provides a human operator with advice on the confirmation and classification of occurred alarm. The input of the system comprises uncertain and incomplete information. In the light of uncertain and incomplete information, different uncertainties laws have been associated with the probabilistic assessment of the system loops which combine data of several sources to reach the ultimate classification. The implemented model used Observe-Orient-Decide-Act loop (OODA) combined with Bayesian networks. Results show that the system can classify the alarms system.
Berghout T, Mouss L-H, Bentrcia T, Elbouchikhi E, Benbouzid M.
A deep supervised learning approach for condition-based maintenance of naval propulsion systems. Ocean EngineeringOcean Engineering [Internet]. 2021;221 :108525.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In the last years, predictive maintenance has gained a central position in condition-based maintenance tasks planning. Machine learning approaches have been very successful in simplifying the construction of prognostic models for health assessment based on available historical labeled data issued from similar systems or specific physical models. However, if the collected samples suffer from lack of labels (small labeled dataset or not enough samples), the process of generalization of the learning model on the dataset as well as on the newly arrived samples (application) can be very difficult. In an attempt to overcome such drawbacks, a new deep supervised learning approach is introduced in this paper. The proposed approach aims at extracting and learning important patterns even from a small amount of data in order to produce more general health estimator. The algorithm is trained online based on local receptive field theories of extreme learning machines using data issued from a propulsion system simulator. Compared to extreme learning machine variants, the new algorithm shows a higher level of accuracy in terms of approximation and generalization under several training paradigms.
Alkebsi EAA, Ameddah H, OUTTAS T, Almutawakel A.
Design of graded lattice structures in turbine blades using topology optimization. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing [Internet]. 2021;34 :370-384.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Designing and manufacturing lattice structures with Topology Optimization (TO) and Additive Manufacturing (AM) techniques is a novel method to create light-weight components with promising potential and high design flexibility. This paper proposes a new design of lightweight-graded lattice structures to replace the internal solid volume of the turbine blade to increase its endurance of high thermal stresses effects. The microstructure design of unit cells in a 3D framework is conducted by using the lattice structure topology optimization (LSTO) technique. The role of the LSTO is to find an optimal density distribution of lattice structures in the design space under specific stress constraints and fill the inner solid part of the blade with graded lattice structures. The derived implicit surfaces modelling is used from a triply periodic minimal surfaces (TPMS) to optimize the mechanical performances of lattice structures. Numerical results show the validity of the proposed method. The effectiveness and robustness of the constructed models are analysed by using finite element analysis. The simulation results show that the graded lattice structures in the improved designs have better efficiency in terms of lightweight (33.41–40.32%), stress (25.52–48.55%) and deformation (7.35–19.58%) compared to the initial design.
Brahimi M, Melkemi K, Boussaad A.
Design of nonstationary wavelets through the positive solution of Bezout’s equation. Journal of Interdisciplinary Mathematics [Internet]. 2021;24 (3) :553-565.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we present a new technique for constructing a nonstationary wavelet. The key idea relies on the following: for each wavelet level, we solve the Bezout’s equation and we propose a positive solution over the interval [–1, 1]. Using the Bernstein’s polynomials we approximate this proposed positive solution with the intention to perform a spectral factorization.
Seddik M-T, KADRI O, Bouarouguene C, Brahimi H.
Detection of Flooding Attack on OBS Network Using Ant Colony Optimization and Machine Learning. Computación y Sistemas [Internet]. 2021;25 (2) :423-433.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Optical burst switching (OBS) has become one of the best and widely used optical networking techniques. It offers more efficient bandwidth usage than optical packet switching (OPS) and optical circuit switching (OCS).However, it undergoes more attacks than other techniques and the Classical security approach cannot solve its security problem. Therefore, a new security approach based on machine learning and cloud computing is proposed in this article. We used the Google Colab platform to apply Support Vector Machine (SVM) and Extreme Learning Machine (ELM)to Burst Header Packet (BHP) flooding attack on Optical Burst Switching (OBS) Network Data Set.
AKSA K, Aitouche S, Bentoumi H, Sersa I.
Developing a Web Platform for the Management of the Predictive Maintenance in Smart Factories. Wireless Personal Communications [Internet]. 2021;119 :1469-1497.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
Industry 4.0 is a tsunami that will invade the whole world. The real challenge of the future factories requires a high degree of reliability both in machinery and equipment. Thereupon, shifting the rudder towards new trends is an inevitable obligation in this fourth industrial revolution where the maintenance system has radically changed to a new one called predictive maintenance 4.0 (PdM 4.0). This latter is used to avoid predicted problems of machines and increase their lifespan taking into account that if machines have not any predicted problem, they will never be checked. However, in order to get successful prediction of any kind of problems, minimizing energy and resources consumption along with saving costs, this PdM 4.0 needs many new emerging technologies such as the internet of things infrastructure, collection and distribution of data from different smart sensors, analyzing/interpreting a huge amount of data using machine/deep learning…etc. This paper is devoted to present the industry 4.0 and its specific technologies used to ameliorate the existing predictive maintenance strategy. An example is given via a web platform to get a clear idea of how PdM 4.0 is applied in smart factories.
Chouia S, Seddik-Ameur N.
Different EDF goodness-of-fit tests for competing risks models. Communications in Statistics-Simulation and ComputationCommunications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation [Internet]. 2021;52 (8) :1-11.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The common used goodeness-of-fit tests are based on the empirical distributions functions (EDF) where distances between empirical and theoretical hypothesized distributions are compared to critical values. The aim of this paper is to provide for different sample sizes, tables of goodness-of-fit critical values of modified Kolmogorov-Smirnov statistic Dn,��, Anderson-Darling statistic A2, Cramer-Von Mises statistic W2,�2, Liao and Shimokawa statistic Ln, and Watson statistic U2 for the competing risks model of Bertholon which is used to describe the reliability of real systems where failure times can have different risks and in medical studies to characterize the survival time of patients who can have risks of death from different causes. The power of these statistics is studied using some alternatives such as the exponential, the inverse Weibull, the exponentiated Weibull and the exponentiated exponential distributions. All the computation are carried out by using matlab software and Monte Carlo method.
BENDJEDDOU YACINE, Abdessemed R, MERABET ELKHEIR.
DIRECTIONAL VIRTUAL FLOW CONTROL OF THE DOUBLE STAR CAGE ASYNCHRONOUS GENERATOR. Revue Roumaine des Sciences Techniques—Série Électrotechnique et Énergétique [Internet]. 2021;66 :71-76.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
This article is devoted to the study of the performance of the double star cage asynchronous generator (GASDE) in isolated site. The control system consists of a GASDE connected to a dc bus and a load at the output of two PWM control rectifiers. A comparative study between the conventional control technique and the adapted control based on the introduction of the SVM- PI-fuzzy and a new flux estimator (virtual stator flux) in order to improve the quality of energy and to attenuate the harmonic of the current.
Ledmi M, Moumen H, Siam A, Haouassi H, Azizi N.
A Discrete Crow Search Algorithm for Mining Quantitative Association Rules. International Journal of Swarm Intelligence Research (IJSIR) [Internet]. 2021;12 (4) :101-124.
Publisher's VersionAbstractAssociation rules are the specific data mining methods aiming to discover explicit relations between the different attributes in a large dataset. However, in reality, several datasets may contain both numeric and categorical attributes. Recently, many meta-heuristic algorithms that mimic the nature are developed for solving continuous problems. This article proposes a new algorithm, DCSA-QAR, for mining quantitative association rules based on crow search algorithm (CSA). To accomplish this, new operators are defined to increase the ability to explore the searching space and ensure the transition from the continuous to the discrete version of CSA. Moreover, a new discretization algorithm is adopted for numerical attributes taking into account dependencies probably that exist between attributes. Finally, to evaluate the performance, DCSA-QAR is compared with particle swarm optimization and mono and multi-objective evolutionary approaches for mining association rules. The results obtained over real-world datasets show the outstanding performance of DCSA-QAR in terms of quality measures.
Mazouz F, Belkacem S, Colak I.
DPC-SVM of DFIG Using Fuzzy Second Order Sliding Mode Approach. International Journal of Smart Grid-ijSmartGrid [Internet]. 2021;5 (4) :174-182.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The direct control power (DPC) of the of the double feed induction generator (DFIG) using conventional controllers based on PI regulators is characterized by poor results: Robustness properties are not guaranteed in the face of parametric uncertainties and strong ripple of the powers. From the best evoked control techniques presented in this field to overcome these drawbacks, we will study some improvement variants such as the use of The second order sliding mode control (SOSMC) developed on the basis of the super twisting torsion algorithm (STA) associated with the fuzzy logic control to obtain (FSOSMC) in order to obtain acceptable performance. Finally, the effectiveness of the planned control system is studied using Matlab/Simulink. The proposed method that not only reduces power ripples, but also improves driving dynamics by making it less sensitive to parameter uncertainty.
Taguelmimt R, Beghdad R.
DS-kNN: An Intrusion Detection System Based on a Distance Sum-Based K-Nearest Neighbors. International Journal of Information Security and Privacy (IJISP) [Internet]. 2021;15 (2) :131-144.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
On one hand, there are many proposed intrusion detection systems (IDSs) in the literature. On the other hand, many studies try to deduce the important features that can best detect attacks. This paper presents a new and an easy-to-implement approach to intrusion detection, named distance sum-based k-nearest neighbors (DS-kNN), which is an improved version of k-NN classifier. Given a data sample to classify, DS-kNN computes the distance sum of the k-nearest neighbors of the data sample in each of the possible classes of the dataset. Then, the data sample is assigned to the class having the smallest sum. The experimental results show that the DS-kNN classifier performs better than the original k-NN algorithm in terms of accuracy, detection rate, false positive, and attacks classification. The authors mainly compare DS-kNN to CANN, but also to SVM, S-NDAE, and DBN. The obtained results also show that the approach is very competitive.
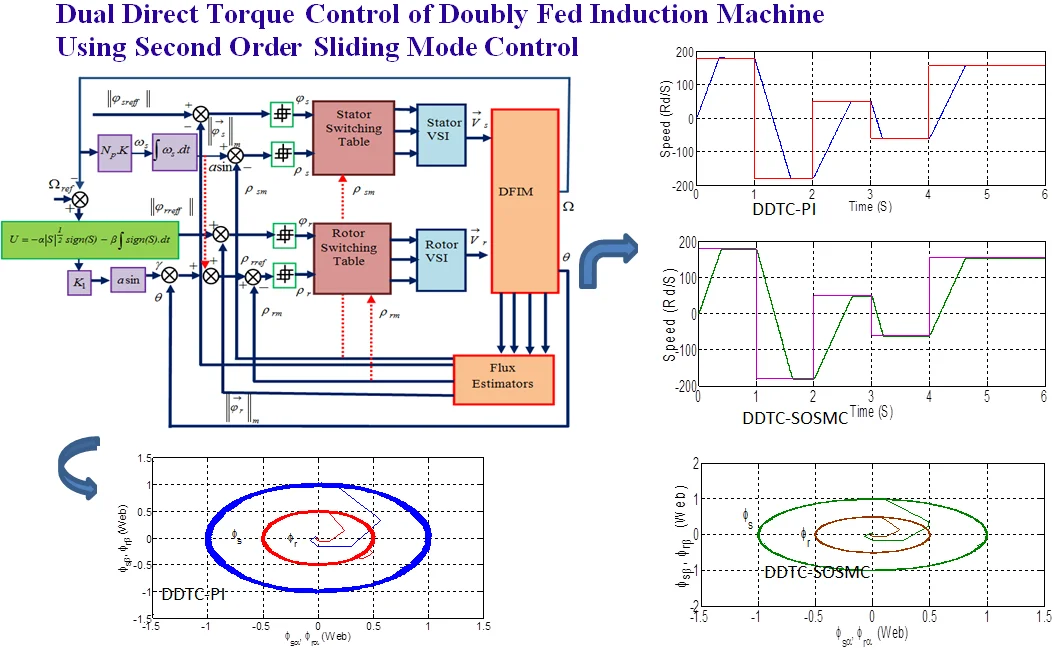
Boumaraf F, BOUTABBA T, Belkacem S.
Dual direct torque control of doubly fed induction machine using second order sliding mode control. Journal of Measurements in Engineering [Internet]. 2021;9 (1) :1-12.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper a dual direct torque control (DDTC) strategy with second-order sliding mode control (SOSMC) controller of the doubly fed Induction motor (DFIM) is presented in order to overcome some drawback such as ripples in torque, flux and to improve dual direct torque control (DDTC) performance toward the electrical parameters variations. This control strategy used in the doubly fed induction machine supplied, coupled by two voltage source inverters in rotor and stator sides witches are linked to two switching tables in order to determined the rotor and stator flux vector control. This controller based on super-twisting algorithm (STA). Comparative results between a classical controller (PI) and the proposed controller can prove the very satisfactory performance and robustness of this new controller.
Aouf A, Bouchala T, Abdou A, Abdelhadi B, Kim SK, Thippeswamy VS, Shivakumaraswamy PM, Chickaramanna SG, Iyengar VM, Das AP.
Eddy Current Probe Configuration for Full Rail Top Surface Inspection. International Information and Engineering Technology Association (IIETA) [Internet]. 2021;20 :65-72.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
In this paper, we have carried out an experimental study of the detection of top rail surface cracks. Firstly, we have highlighted the inability to inspect the entire rail head surface by a single sensor with a single scan. To overcome this inspection inability, we have proposed a multisensor system composed of three differential probes arranged within a specific configuration. The yielded results showed the efficiency and the robustness of the proposed configuration in the detection of cracks regardless its size, orientation and location.
Beghzim H, Karech T, Bouzid T.
The Effect of Faults on the Behaviour of the Earth Dam–Case Study of the Ourkiss Dam. (Preprint). Research Square [Internet]. 2021.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The analysis of the failure due to the effect of the propagation of normal and reversed faults with different angles of inclination and by sliding through the Ourkiss dam isstudied numerically. Mainly at the end of construction and at the highest water level, for this purpose the non-linear finite difference method is used considering four fault angles of inclination, activated at the center of the base of the embankment.
The results of the study show that the shear stress values increase with the increase of the vertical base displacement imposed in both conditions of the dam state, and this for both normal and overturned faults.
Zine A, Kadid A, Zatar A.
Effect of Masonry Infill Panels on the Seismic Response of Reinforced Concrete Frame Structures. Civil Engineering Journal [Internet]. 2021;7 (11) :1853-1867.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The present work concerns the numerical investigation of reinforced concrete frame buildings containing masonry infill panel under seismic loading that are widely used even in high seismicity areas. In seismic zones, these frames with masonry infill panels are generally considered as higher earthquake risk buildings. As a result there is a growing need to evaluate their level of seismic performance. The numerical modelling of infilled frames structures is a complex task, as they exhibit highly nonlinear inelastic behaviour, due to the interaction of the masonry infill panel and the surrounding frame. The available modelling approaches for masonry infill can be grouped into two principal types; Micro models and Macro models. A two dimensional model of the structure is used to carry out non-linear static analysis. Beams and columns are modelled as non-linear with lumped plasticity where the hinges are concentrated at both ends of the beams and the columns. This study is based on structures with design and detailing characteristics typical of Algerian construction model. In this regard, a non-linear pushover analysis has been conducted on three considered structures, of two, four and eight stories. Each structure is analysed as a bare frame and with two different infill configurations (totally infilled, and partially infilled). The main results that can be obtained from a pushover analysis are the capacity curves and the distribution of plastic hinges in structures. The addition of infill walls results in an increase in both the rigidity and strength of the structures. The results indicate that the presence of non-structural masonry infills can significantly modify the seismic response of reinforced concrete "frames". The initial rigidity and strength of the fully filled frame are considerably improved and the patterns of the hinges are influenced by structural elements type depending on the dynamic characteristics of the structures.
Rahem A, Djarir Y, Noureddine L, Tayeb B.
Effect of masonry infill walls with openings on nonlinear response of steel frames. Civil Engineering Journal [Internet]. 2021;7 (2) :278-291.
Publisher's VersionAbstract
The infill walls are usually considered as nonstructural elements and, thus, are not taken into account in analytical models. However, numerous researches have shown that they can significantly affect the seismic response of the structures. The aim of the present study is to examine the role of masonry infill on the damage response of steel frame without and with various types of openings systems subjected to nonlinear static analysis and nonlinear time history analysis. For the purposes of the above investigation, a comprehensive assessment is conducted using twelve typical types of steel frame without masonry, with full masonry and with different heights and widths of openings. The results revealed that the influence of the successive earthquake phenomenon on the structural damage is larger for the infill buildings compared to the bare structures. Furthermore, when buildings with masonry infill are analyzed for seismic sequences, it is of great importance to account for the orientation of the seismic motion. The nonlinear static response indicated that the opening area has an influence on the maximal strength, the ductility and the initial rigidity of these frames. But the shape of the opening will not influence the global behavior. Then, the nonlinear time history analysis indicates that the global displacement is greatly decreased and even the behavior of the curve is affected by the earthquake intensity when opening is considered.